JavaScript 開發者學習 Dart
本指南旨在利用您的 JavaScript 程式設計知識來學習 Dart。它展示了兩種語言之間的主要異同,並介紹了 JavaScript 不支援的 Dart 概念。作為一名 JavaScript 開發者,Dart 應該會感覺相當熟悉,因為兩種語言共享許多概念。
與 JavaScript 類似,Dart 執行在事件迴圈上,因此兩種語言執行程式碼的方式相似。例如,Future(JavaScript 中的 Promise)和 async/await 語法等非同步概念非常相似。
與 JavaScript 不同,Dart 是強型別語言。如果您使用過 TypeScript 或 Flow,這應該會簡化 Dart 的學習。如果您主要使用純 JavaScript,這可能需要一些適應。透過強型別,Dart 在編譯前捕獲許多在 JavaScript 程式碼中可能存在的錯誤。
Dart 預設啟用空安全。JavaScript 不支援空安全。作為一名 JavaScript 開發者,學習如何編寫空安全程式碼可能需要一段時間,但其好處是能更好地防止空引用異常,這些異常甚至在編譯 Dart 程式碼之前就能被檢測到。(從而避免在對 JavaScript 變數進行操作時,該變數結果為 null 時出現的那些可怕的 TypeError。)
約定與 Linting
#JavaScript 和 Dart 都擁有 Linting 工具來強制執行標準約定。雖然 JavaScript 提供了許多工具、標準和配置,但 Dart 擁有一套官方的佈局和樣式約定,以及一個 Linter 來簡化合規性。Dart 分析器會對程式碼進行 Linting,並提供更多分析功能。要自定義專案的 Lint 規則,請遵循 自定義靜態分析 指南。
Dart 提供了 dart fix 來查詢並修復錯誤。
Dart 還提供了一個程式碼格式化工具,類似於 JavaScript 工具,例如 Prettier。要在任何 Dart 專案中格式化程式碼,請在命令列中執行 dart format。Dart 和 Flutter 的 IDE 外掛也提供了此功能。
Dart 支援在集合、引數或實參的逗號分隔列表中使用尾隨逗號。當您新增尾隨逗號時,格式化程式會將每個列表項放在單獨的行上。當您認為列表將來可能包含更多項時,請新增尾隨逗號。避免僅僅為了格式化效果而新增尾隨逗號。
JavaScript 僅在列表和對映字面量中支援尾隨逗號。
內建型別
#JavaScript 和 Dart 都將資料分類為 型別。每個變數都有一個關聯的型別。型別決定了變數可以儲存的值的種類以及可以對這些值執行的操作。Dart 與 JavaScript 的不同之處在於,它為每個表示式和變數分配一個靜態型別。靜態型別預測變數值或表示式值的執行時型別。這意味著 Dart 應用程式具有健全的靜態型別。
JavaScript 提供原始型別 num、string 和 boolean 以及 null 值,還有 陣列 和 Map 型別。
Dart 支援以下內建型別:
- 數字 (
num,int,double) - 字串 (
String) - 布林值 (
bool) - 列表 (
List,也稱為陣列) - 集合 (
Set) - 對映 (
Map) - 符號 (
Symbol) null值 (Null)
要了解更多資訊,請查閱 Dart 語言之旅 中的 內建型別。
Dart 中所有非 Null 型別都是 Object 的子型別。所有值也都是物件。Dart 不像 JavaScript 那樣使用“原始型別”。相反,Dart 會規範化或範化數字、布林值和 null 值。這意味著數值為 1 的 int 值只有一個。
例如:相等運算子 == 和 identical() 方法對於相同數值型別的相同值返回 true。請檢視以下程式碼中所示的示例:
var a = 2;
var b = 1 + 1;
print(a == b); // Prints true
print(identical(a, b)); // Prints true; only one "2" object exists原始型別
#本節介紹 Dart 如何表示 JavaScript 的原始型別。
數字
#Dart 有三種用於儲存數字的資料型別:
num- 相當於 JavaScript 中的通用數字型別。
int- 不帶小數部分的數值。
double- 任何 64 位(雙精度)浮點數。
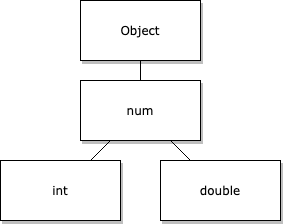
Dart API 將所有這些型別作為類包含。int 和 double 型別都以 num 作為它們的父類。
由於 Dart 將數字視為物件,因此數字可以將其自身的實用函式作為物件方法暴露。您無需使用額外的物件即可將函式應用於數字。
例如,將 double 四捨五入為整數:
let rounded = Math.round(2.5);var rounded = 2.5.round();字串
#Dart 中的字串工作方式與 JavaScript 中的字串類似。要編寫字串字面量,請將其用單引號 (') 或雙引號 (") 括起來。大多數 Dart 開發者使用單引號,但語言沒有強制規定標準。如果您不想在字串中轉義單引號,請使用雙引號。
var a = 'This is a string.';轉義特殊字元
#要在字串中包含具有其他含義的字元,例如用於字串插值的 $,您必須轉義該字元。Dart 中轉義特殊字元的工作方式與 JavaScript 和大多數其他語言類似。要轉義特殊字元,請在該字元前加上反斜槓字元 (\)。
以下程式碼顯示了一些示例。
final singleQuotes = 'I\'m learning Dart'; // I'm learning Dart
final doubleQuotes = "Escaping the \" character"; // Escaping the " character
final dollarEscape = 'The price is \$3.14.'; // The price is $3.14.
final backslashEscape = 'The Dart string escape character is \\.';
final unicode = '\u{1F60E}'; // 😎, Unicode scalar U+1F60E字串插值
#JavaScript 支援模板字面量。它們使用反引號 (`) 字元分隔符的原因如下:
- 允許多行字串
- 用嵌入表示式插值字串
- 建立稱為帶標籤模板的特殊構造
在 Dart 中,您無需使用反引號將字串括起來即可連線字串或在字串字面量中使用插值。
要了解更多資訊,請查閱 Dart 語言之旅中的 字串。
與 JavaScript 模板字面量一樣,您可以使用 ${<expression>} 語法將表示式插入到字串字面量中。Dart 使用此語法,並且當表示式使用單個識別符號時,允許您省略花括號。
var food = 'bread';
var str = 'I eat $food'; // I eat bread
var str = 'I eat ${food}'; // I eat bread字串連線和多行宣告
#在 JavaScript 中,您可以使用模板字面量定義多行字串。Dart 有兩種定義多行字串的方式。
- 使用隱式字串連線:Dart 會連線任何相鄰的字串字面量,即使它們分佈在多行上。dart
final s1 = 'String ' 'concatenation' " even works over line breaks."; - 使用多行字串字面量:當字串兩邊使用三個引號(單引號或雙引號)時,字面量可以跨越多行。dart
final s2 = ''' You can create multiline strings like this one. '''; final s3 = """ This is also a multiline string.""";
相等性
#當兩個字串包含相同的程式碼單元序列時,Dart 認為它們相等。要確定兩個字串是否具有相同的序列,請使用等於運算子 (==)。
final s1 = 'String '
'concatenation'
" works even over line breaks.";
assert(s1 ==
'String concatenation works even over '
'line breaks.');布林值
#Dart 和 JavaScript 中的布林值都表示二元條件。這兩個值表示一個值或表示式是 true 還是 false。您可以使用字面量 true 和 false 返回這些值,或者使用 x < 5 或 y == null 等表示式生成它們。
let isBananaPeeled = false;var isBananaPeeled = false;變數
#Dart 中的變數工作方式與 JavaScript 中的變數類似,但有兩個例外:
- 每個變數都有一個型別。
- Dart 將所有變數的作用域限制在塊級別,就像 JavaScript 中的
let和const變數一樣。
Dart 變數透過以下兩種方式之一獲取其型別:
- 宣告:在宣告中寫入的型別。
- 推斷:用於初始化變數的表示式。根據慣例,當分析器可以推斷型別時,請使用
var或final。
// Declare and initialize a variable at once
let name = "bob";// Declare a variable with a specific type
// when you don't provide an initial value
String name;
// Declare and initialize a variable
// at the same time and Dart infers
// the type
var name = 'bob';變數只能接受其型別的值。
var name = 'bob';
name = 5; // Forbidden, as `name` has type `String`.如果您不提供初始值或顯式型別,Dart 會將變數的型別推斷為包羅永珍的 dynamic 型別。
與 JavaScript 變數一樣,您可以將任何值賦值給使用 dynamic 型別的 Dart 變數。
// Declare a variable
let name;
// Initialize the variable
name = "bob";// Declare a variable without a type or assigned value
// and Dart infers the 'dynamic' type
var name;
// Initialize the variable and the type remains `dynamic`
name = 'bob';
name = 5; // Allowed, as `name` has type `dynamic`.final 與 const
#JavaScript 和 Dart 都使用變數修飾符。兩者都使用 const,但在 const 的工作方式上有所不同。JavaScript 使用 const 的地方,Dart 使用 final。
當您向 Dart 變數新增 final 或向 JavaScript 變數新增 const 時,您必須在其他程式碼讀取其值之前初始化該變數。一旦初始化,您就不能更改這些變數的引用。
當 Dart 使用 const 時,它指的是在編譯時建立的特殊值。Dart 使用有限的表示式來建立這些不可變值。這些表示式不能有副作用。在這些條件下,編譯器可以預測常量變數或表示式的精確值,而不僅僅是其靜態型別。
final String name;
// Cannot read name here, not initialized.
if (useNickname) {
name = "Bob";
} else {
name = "Robert";
}
print(name); // Properly initialized here.在 Dart 中,常量變數必須包含常量值。非常量變數可以包含常量值,您也可以將其標記為 const。
var foo = const [];
// foo is not constant, but the value it points to is.
// You can reassign foo to a different list value,
// but its current list value cannot be altered.
const baz = []; // Equivalent to `const []`同樣,類可以有自己的 const 建構函式,用於生成不可變例項。
您不能在 JavaScript 或 Dart 中修改 const 變數。JavaScript 確實允許您修改 const 物件的欄位,但 Dart 不允許。
要了解更多資訊,請參閱類 部分。
空安全
#與 JavaScript 不同,Dart 支援空安全。在 Dart 中,所有型別預設都是非可空的。這使得 Dart 開發者受益,因為 Dart 在編寫程式碼時而非執行時捕獲空引用異常。
可空型別與非可空型別
#以下程式碼示例中的任何變數都不能為 null。
// In null-safe Dart, none of these can ever be null.
var i = 42; // Inferred to be an int.
String name = getFileName();
final b = Foo(); // Foo() invokes a constructor要指示變數可能具有 null 值,請在其型別宣告中新增 ?:
int? aNullableInt = null;任何其他型別宣告,例如函式宣告,也是如此:
String? returnsNullable() {
return random.nextDouble() < 0.5
? 'Sometimes null!'
: null;
}
String returnsNonNullable() {
return 'Never null!';
}空值感知運算子
#Dart 支援多種運算子來處理可空性。與 JavaScript 類似,Dart 支援空賦值運算子 (??=)、空合併運算子 (??) 和可選鏈運算子 (?.)。這些運算子的工作方式與 JavaScript 相同。
! 運算子
#在可空變數或表示式可能非空的情況下,您可以使用 (!) 運算子告訴編譯器抑制任何編譯時錯誤。將此運算子放在表示式之後。
不要將其與 Dart 的非 (!) 運算子混淆,後者使用相同的符號但放在表示式之前。
int? a = 5;
int b = a; // Not allowed.
int b = a!; // Allowed.在執行時,如果某個值結果為 null,則會發生執行時錯誤。
與 ?. 運算子類似,在訪問物件的屬性或方法時使用 ! 運算子。
myObject!.someProperty;
myObject!.someMethod();如果在執行時 myObject 為 null,則會發生執行時錯誤。
函式
#雖然 Dart 的函式工作方式與 JavaScript 中的對應函式大致相同,但它們確實有一些額外的功能,並且在宣告時有一些細微的語法差異。與 JavaScript 類似,您幾乎可以在任何地方宣告函式,無論是在頂層、作為類欄位還是在區域性作用域中。
// On the top level
function multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
// As a class field
class Multiplier {
multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
}
// In a local scope
function main() {
function multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
console.log(multiply(3, 4));
}// On the top level
int multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
// As a class field
class Multiplier {
multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
}
// In a local scope
main() {
multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
print(multiply(3, 4));
}箭頭語法
#Dart 和 JavaScript 都支援箭頭語法 (=>),但它們支援的方式有所不同。在 Dart 中,您只能在函式包含單個表示式或 return 語句時使用箭頭語法。
例如,以下 isNoble 函式是等效的:
bool isNoble(int atomicNumber) {
return _nobleGases[atomicNumber] != null;
}bool isNoble(int atomicNumber) => _nobleGases[atomicNumber] != null;引數
#在 JavaScript 中,所有引數可以是位置引數。預設情況下,Dart 要求您將所有引數作為實參傳遞給函式。
int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
main() {
multiply(3, 5); // Valid. All parameters are provided.
multiply(3); // Invalid. All parameters must be provided.
}這在兩種情況下可能會改變:
- 位置引數被標記為可選。
- 引數是命名引數且未標記為必需。
要定義可選的位置引數,請將其放在任何必需位置引數之後的方括號中。您不能在可選引數之後跟必需引數。
由於空安全,可選的位置引數必須具有預設值或被標記為可空。要了解更多資訊,請參閱前面關於 空安全 的部分。
以下程式碼包含一個有效示例和兩個無效示例,它們定義了可選的位置引數的函式。
// Valid: `b` has a default value of 5. `c` is marked as nullable.
multiply(int a, [int b = 5, int? c]) {
...
}
// Invalid: a required positional parameter follows an optional one.
multiply(int a, [int b = 5], int c) {
...
}
// Invalid: Neither optional positional parameter has a default
// value or has been flagged as nullable.
multiply(int a, [int b, int c]) {
...
}以下示例展示瞭如何呼叫帶可選引數的函式:
multiply(int a, [int b = 5, int? c]) {
...
}
main() {
// All are valid function calls.
multiply(3);
multiply(3, 5);
multiply(3, 5, 7);
}Dart 支援命名引數。這些引數不必按照定義順序提供,與位置引數不同。您可以透過名稱引用它們。預設情況下,它們是可選的,除非被標記為必需。命名引數透過花括號括起來定義。您可以將命名引數與必需的位置引數結合使用——在這種情況下,命名引數總是放在位置引數之後。呼叫帶有命名引數的函式時,透過在傳遞的值前加上引數名稱,並用冒號分隔來傳遞值。例如,f(namedParameter: 5)。
同樣,在空安全的情況下,未標記為必需的命名引數要麼需要有預設值,要麼需要標記為可空。
以下程式碼定義了一個帶命名引數的函式:
// Valid:
// - `a` has been flagged as required
// - `b` has a default value of 5
// - `c` is marked as nullable
// - Named parameters follow the positional one
multiply(bool x, {required int a, int b = 5, int? c}) {
...
}以下示例呼叫帶命名引數的函式:
// All are valid function calls.
// Beyond providing the required positional parameter:
multiply(false, a: 3); // Only provide required named parameters
multiply(false, a: 3, b: 9); // Override default value of `b`
multiply(false, c: 9, a: 3, b: 2); // Provide all named parameters out of order一等函式
#JavaScript 和 Dart 都將函式視為一等公民。這意味著 Dart 將函式視為任何其他物件。例如,以下程式碼展示瞭如何將函式作為引數傳遞給另一個函式:
void printElement(int element) {
print(element);
}
var list = [1, 2, 3];
// Pass printElement as a parameter.
list.forEach(printElement);匿名函式
#JavaScript 和 Dart 都支援 匿名函式,即沒有名稱的函式。與命名函式一樣,您可以像傳遞任何其他值一樣傳遞匿名函式。例如,將匿名函式儲存在變數中,將其作為引數傳遞給另一個函式,或從另一個函式返回它們。
JavaScript 有兩種宣告匿名函式的方式:
- 使用標準函式表示式
- 使用箭頭語法
同樣,Dart 也有兩種宣告匿名函式的方式。兩者都以類似於 JavaScript 箭頭表示式的方式工作。Dart 的匿名函式不支援常規函式表示式所附帶的額外功能。例如,JavaScript 支援函式表示式充當建構函式,或建立到 `this` 的自定義繫結。
要了解更多資訊,請參閱類 部分。
// A regular function expression
// assigned to a variable
let funcExpr = function(a, b) {
return a * b;
}
// The same anonymous function
// expressed as an arrow
// function with curly braces.
let arrowFuncExpr = (a, b) => {
return a * b;
}
// An arrow function with only
// one return statement as
// its contents does not
// require a block.
let arrowFuncExpr2 = (a, b) => a * b;// Assign an anonymous function
// to a variable.
var blockFunc =
optionalCallback ?? (int a, int b) {
return a * b;
};
// For an expression with only a return statement,
// you can use the arrow syntax:
var singleFunc = (int a, int b) => a * b;與 JavaScript 一樣,您可以將匿名函式傳遞給其他函式。開發者在使用 map 函式處理陣列和列表時,通常會傳遞匿名函式:
// returns [4, 5, 6]
[1, 2, 3].map(e => e + 3);
// returns [5, 7, 9]
[1, 2, 3].map(e => {
e *= 2;
return e + 3;
});// returns [4, 5, 6]
[1, 2, 3].map((e) => e + 3).toList();
// returns [5, 7, 9]
var list2 = [1, 2, 3].map((e) {
e *= 2;
return e + 3;
}).toList();生成器函式
#兩種語言都支援 生成器函式。這些函式返回一個可迭代的項集合,這些項的計算是為了避免不必要的工作。
要在 Dart 中編寫生成器函式,請在函式引數後新增 sync* 關鍵字,並返回一個 Iterable。使用 yield 關鍵字將項新增到最終的可迭代物件中,或者使用 yield* 新增整個項集。
以下示例展示瞭如何編寫一個基本的生成器函式:
function* naturalsTo(n) {
let k = 0;
while (k < n) {
yield k++;
}
}
// Returns [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
for (let value of naturalsTo(5)) {
console.log(value);
}Iterable<int> naturalsTo(int n) sync* {
int k = 0;
while (k < n) {
yield k++;
}
}
// Returns an iterable with [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
print(naturalsTo(5).toList());function* doubleNaturalsTo(n) {
let k = 0;
while (k < n) {
yield* [k, k];
k++;
}
}
// Returns [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]
for (let value of doubleNaturalsTo(3)) {
console.log(value);
}Iterable<int> doubleNaturalsTo(int n) sync* {
int k = 0;
while (k < n) {
yield* [k, k];
k++;
}
}
// Returns an iterable with [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]
print(doubleNaturalsTo(3));您還可以定義非同步生成器函式,它們返回 Stream 而不是 Iterable。在即將到來的非同步 部分了解更多。
語句
#本節描述 JavaScript 和 Dart 之間語句的差異。
控制流 (if/else, for, while, switch)
#大多數控制語句的工作方式與它們的 JavaScript 對應物類似。有些對於集合 有額外用途。
迭代
#雖然 JavaScript 和 Dart 都有 for-in 迴圈,但它們的行為不同。
JavaScript 的 for-in 迴圈迭代物件的屬性。要迭代 JavaScript 可迭代物件的元素,您必須使用 for-of 或 Array.forEach()。Dart 的 for-in 迴圈工作方式類似於 JavaScript 的 for-of。
以下示例展示瞭如何迭代集合並打印出每個元素:
for (const element of list) {
console.log(element);
}for (final element in list) {
print(element);
}Switch
#在 switch 語句中使用 continue 時,您可以將其與放在 case 上的標籤結合使用:
switch (testEnum) {
case TestEnum.A:
print('A');
continue b;
b:
case TestEnum.B:
print('B');
break;
}運算子
#Dart 和 JavaScript 都包含預定義運算子。兩種語言都不支援新增新運算子。Dart 支援使用 operator 關鍵字過載一些現有運算子。例如:
class Vector {
final double x;
final double y;
final double z;
Vector(this.x, this.y, this.z);
Vector operator +(Vector other) => Vector(
x + other.x,
y + other.y,
z + other.z,
);
Vector operator *(double scalar) => Vector(
x * scalar,
y * scalar,
z * scalar,
);
}算術運算子
#兩種語言的相等和關係運算符幾乎相同,如下表所示:
| 含義 | JavaScript 運算子 | Dart 運算子 |
|---|---|---|
| 加 | + | + |
| 減 | - | - |
| 一元減號,也稱作求反 | -expr | -expr |
| 乘 | * | * |
| 除 | / | / |
| 返回整數結果的除法 | ~/ | |
| 獲取整數除法的餘數 (模) | % | % |
x = x + 1 (表示式值為 x + 1) | ++x | ++x |
x = x + 1 (表示式值為 x) | x++ | x++ |
x = x - 1 (表示式值為 x - 1) | --x | --x |
x = x - 1 (表示式值為 x) | x-- | x-- |
例如
assert(2 + 3 == 5);
assert(2 - 3 == -1);
assert(2 * 3 == 6);
assert(5 / 2 == 2.5); // Result is a double
assert(5 ~/ 2 == 2); // Result is an int
assert(5 % 2 == 1); // Remainder
a = 0;
b = ++a; // Increment a before b gets its value.
assert(a == b); // 1 == 1
a = 0;
b = a++; // Increment a AFTER b gets its value.
assert(a != b); // 1 != 0
a = 0;
b = --a; // Decrement a before b gets its value.
assert(a == b); // -1 == -1
a = 0;
b = a--; // Decrement a AFTER b gets its value.
assert(a != b); // -1 != 0您可能已經注意到 Dart 還包含一個 ~/ 運算子(稱為截斷除法運算子),它將雙精度浮點數相除並輸出一個向下取整的整數。
assert(25 == 50.4 ~/ 2);
assert(25 == 50.6 ~/ 2);
assert(25 == 51.6 ~/ 2);相等和關係運算符
#兩種語言的相等和關係運算符工作方式相同:
| 含義 | JavaScript 運算子 | Dart 運算子 |
|---|---|---|
| 嚴格相等 | === | == |
| 抽象相等 | == | |
| 嚴格不相等 | !== | != |
| 抽象不相等 | != | |
| 大於 | > | > |
| 小於 | < | < |
| 大於或等於 | >= | >= |
| 小於或等於 | <= | <= |
JavaScript 的 == 和 != 運算子沒有等效項。
例如
assert(2 == 2);
assert(2 != 3);
assert(3 > 2);
assert(2 < 3);
assert(3 >= 3);
assert(2 <= 3);型別測試運算子
#兩種語言中測試運算子的實現方式略有不同:
| 含義 | JavaScript 運算子 | Dart 運算子 |
|---|---|---|
| 型別轉換 | x as T | |
| 如果物件具有指定型別則為 true | x instanceof T | x is T |
| 如果物件缺乏指定型別則為 true | !(x instanceof T) | x is! T |
如果 obj 實現了 T 指定的介面,則 obj is T 的結果為 true。例如,obj is Object? 總是 true。
使用型別轉換運算子 (as) 來確保值具有特定型別。如果您知道物件將具有該型別,編譯器可以使用它。
例如
(person as Employee).employeeNumber = 4204583;如果您不知道物件是 T 型別,那麼在使用物件之前使用 is T 來檢查型別。
在 Dart 中,區域性變數的型別在 if 語句的作用域內更新。例項變數則不是這樣。
if (person is Employee) {
person.employeeNumber = 4204583;
}邏輯運算子
#您可以使用邏輯運算子反轉或組合布林表示式。兩種語言的邏輯運算子是相同的。
| 含義 | JavaScript 運算子 | Dart 運算子 |
|---|---|---|
| 反轉下一個表示式(將 false 變為 true,反之亦然) | !x | !x |
| 邏輯或 | || | || |
| 邏輯與 | && | && |
JavaScript 允許在需要布林值的地方使用任何值。然後它會將這些值轉換為 true 或 false。JavaScript 將空字串和數字 0 視為“falsy”值。Dart 允許 bool 值用於條件和作為邏輯運算子的運算元。
例如
if (!done && (col == 0 || col == 3)) {
// ...Do something...
}位運算和移位運算子
#您可以使用位運算和移位運算子對整數的單個位進行操作。兩種語言的運算子幾乎相同,如下表所示:
| 含義 | JavaScript 運算子 | Dart 運算子 |
|---|---|---|
| 按位與 | & | & |
| 按位或 | | | | |
| 按位異或 | ^ | ^ |
| 一元按位補碼(0 變為 1;1 變為 0) | ~expr | ~expr |
| 左移 | << | << |
| 右移 | >> | >> |
| 無符號右移 | >>> | >>> |
例如
final value = 0x22;
final bitmask = 0x0f;
assert((value & bitmask) == 0x02); // AND
assert((value & ~bitmask) == 0x20); // AND NOT
assert((value | bitmask) == 0x2f); // OR
assert((value ^ bitmask) == 0x2d); // XOR
assert((value << 4) == 0x220); // Shift left
assert((value >> 4) == 0x02); // Shift right
assert((-value >> 4) == -0x03); // Shift right
assert((value >>> 4) == 0x02); // Unsigned shift right
assert((-value >>> 4) > 0); // Unsigned shift right條件運算子
#Dart 和 JavaScript 都包含用於評估表示式的條件運算子 (?:)。一些開發者將其稱為三元運算子,因為它需要三個運算元。由於 Dart 還有另一個接受三個運算元的運算子 ([]=),所以將此運算子 (?:) 稱為條件運算子。此運算子對錶達式的作用類似於 if-else 對語句的作用。
let visibility = isPublic ? "public" : "private";final visibility = isPublic ? 'public' : 'private';賦值運算子
#使用 (=) 運算子來賦值。
// Assign value to a
a = value;此運算子還有一個空值感知變體 (??=)。
要了解更多資訊,請參閱空賦值 運算子部分。
JavaScript 和 Dart 都包含在表示式中計算並將新值賦給變數的運算子。這些賦值運算子使用右側值和變數初始值作為運算元。
下表列出了這些賦值運算子:
| 運算子 | 描述 |
|---|---|
= | 賦值 |
+= | 加法賦值 |
-= | 減法賦值 |
*= | 乘法賦值 |
/= | 除法賦值 |
~/= | 截斷除法賦值 |
%= | 取餘 (模) 賦值 |
>>>= | 無符號右移賦值 |
^= | 按位異或賦值 |
<<= | 左移賦值 |
>>= | 右移賦值 |
&= | 按位與賦值 |
|= | 按位或賦值 |
JavaScript 不支援 ~/= 賦值運算子。
var a = 5;
a *= 2; // Multiply `a` by 2 and assign the result back to a.
print(a); // `a` is now 10.級聯 (.. 運算子)
#Dart 允許您在單個物件上鍊接多個方法呼叫、屬性賦值或兩者。Dart 將此稱為級聯,並使用級聯語法 (..) 來執行此操作。
JavaScript 缺乏這種語法。
以下示例展示瞭如何使用級聯語法在新構造的物件上鍊接多個方法:
var animal = Animal() // Sets multiple properties and methods
..name = "Bob"
..age = 5
..feed()
..walk();
print(animal.name); // "Bob"
print(animal.age); // 5為了使第一個級聯語法為空值感知,請將其寫為 ?..。
var result = maybePerson
?..employment = employer
..salary = salary;如果 maybePerson 值為 null,Dart 會忽略整個級聯操作。
集合
#本節涵蓋 Dart 中的一些集合型別,並將其與 JavaScript 中的類似型別進行比較。
列表
#Dart 編寫列表字面量的方式與 JavaScript 陣列相同。Dart 將列表用方括號括起來,並用逗號分隔值。
// Initialize list and specify full type
final List<String> list1 = <String>['one', 'two', 'three'];
// Initialize list using shorthand type
final list2 = <String>['one', 'two', 'three'];
// Dart can also infer the type
final list3 = ['one', 'two', 'three'];以下程式碼示例概述了您可以在 Dart List 上執行的基本操作。以下示例展示瞭如何使用索引運算子從 List 中檢索值。
final fruits = <String>['apple', 'orange', 'pear'];
final fruit = fruits[1];使用 add 方法將值新增到 List 的末尾。使用 addAll 方法新增另一個 List。
final fruits = <String>['apple', 'orange', 'pear'];
fruits.add('peach');
fruits.addAll(['kiwi', 'mango']);使用 insert 方法在特定位置插入值。使用 insertAll 方法在特定位置插入另一個 List。
final fruits = <String>['apple', 'orange', 'pear'];
fruits.insert(0, 'peach');
fruits.insertAll(0, ['kiwi', 'mango']);結合索引和賦值運算子更新 List 中的值。
final fruits = <String>['apple', 'orange', 'pear'];
fruits[2] = 'peach';使用以下方法之一從 List 中移除項:
final fruits = <String>['apple', 'orange', 'pear'];
// Remove the value 'pear' from the list.
fruits.remove('pear');
// Removes the last element from the list.
fruits.removeLast();
// Removes the element at position 1 from the list.
fruits.removeAt(1);
// Removes the elements with positions greater than
// or equal to start (1) and less than end (3) from the list.
fruits.removeRange(1, 3);
// Removes all elements from the list that match the given predicate.
fruits.removeWhere((fruit) => fruit.contains('p'));使用 length 獲取 List 中的值數量。
final fruits = <String>['apple', 'orange', 'pear'];
assert(fruits.length == 3);使用 isEmpty 檢查 List 是否為空。
var fruits = [];
assert(fruits.isEmpty);使用 isNotEmpty 檢查 List 是否不為空。
final fruits = <String>['apple', 'orange', 'pear'];
assert(fruits.isNotEmpty);填充
#Dart 的 List 類包含一種建立每個項都具有相同值的 List 的方法。此 filled 建構函式建立一個大小為 n 且帶有一個預設值的固定長度列表。以下示例建立了一個包含 3 個項的列表:
final list1 = List.filled(3, 'a'); // Creates: [ 'a', 'a', 'a' ]- 預設情況下,您不能從該列表中新增或移除元素。若要允許此列表新增或移除元素,請在引數列表末尾新增
, growable: true。 - 您可以使用索引值訪問和更新此列表的元素。
生成
#Dart 的 List 類包含一種建立遞增值列表的方法。此 generate 建構函式建立了一個大小為 n 的固定長度列表,並帶有一個用於構建元素值的模板。此模板將索引作為引數。
// Creates: [ 'a0', 'a1', 'a2' ]
final list1 = List.generate(3, (index) => 'a$index');集合
#與 JavaScript 不同,Dart 支援使用字面量定義 Set。Dart 定義 Set 的方式與列表相同,但使用花括號而非方括號。Set 是無序集合,只包含唯一項。Dart 使用雜湊碼強制執行這些項的唯一性,這意味著物件需要雜湊值才能儲存在 Set 中。
以下程式碼片段展示瞭如何初始化一個 Set:
final abc = {'a', 'b', 'c'};建立空 Set 的語法一開始可能看起來令人困惑,因為指定空花括號 ({}) 會導致建立一個空 Map。要建立空 Set,請在 {} 宣告前加上型別引數或將 {} 賦值給 Set 型別的變數:
final names = <String>{};
// Set<String> names = {}; // This works, too.
// final names = {}; // Creates an empty map, not a set.以下示例概述了您可以在 Dart Set 上執行的基本操作。
使用 add 方法將值新增到 Set。使用 addAll 方法新增多個值:
final fruits = {'apple', 'orange', 'pear'};
fruits.add('peach');
fruits.addAll(['kiwi', 'mango']);使用 Set 中的以下方法之一從集合中移除內容:
final fruits = {'apple', 'orange', 'pear'};
// Remove the value 'pear' from the set.
fruits.remove('pear');
// Remove all elements in the supplied list from the set.
fruits.removeAll(['orange', 'apple']);
// Removes all elements from the list that match the given predicate.
fruits.removeWhere((fruit) => fruit.contains('p'));使用 length 獲取 Set 中的值數量。
final fruits = {'apple', 'orange', 'pear'};
assert(fruits.length == 3);使用 isEmpty 檢查 Set 是否為空。
var fruits = <String>{};
assert(fruits.isEmpty);使用 isNotEmpty 檢查 Set 是否不為空。
final fruits = {'apple', 'orange', 'pear'};
assert(fruits.isNotEmpty);對映
#Dart 中的 Map 型別類似於 JavaScript 中的 Map 型別。兩種型別都將鍵與值關聯。如果所有鍵都具有相同型別,則鍵可以是任何物件型別。此規則也適用於值。每個鍵最多出現一次,但您可以多次使用相同的值。
Dart 的字典基於雜湊表。這意味著鍵需要是可雜湊的。每個 Dart 物件都包含一個雜湊。
考慮以下使用字面量建立的簡單 Map 示例:
final gifts = {
'first': 'partridge',
'second': 'turtle doves',
'fifth': 'golden rings'
};
final nobleGases = {
2: 'helium',
10: 'neon',
18: 'argon',
};以下程式碼示例概述了您可以在 Dart Map 上執行的基本操作。以下示例展示瞭如何使用索引運算子從 Map 中檢索值。
final gifts = {'first': 'partridge'};
final gift = gifts['first'];使用 containsKey 方法檢查 Map 是否包含鍵。
final gifts = {'first': 'partridge'};
assert(gifts.containsKey('fifth'));使用索引賦值運算子 ([]=) 在 Map 中新增或更新條目。如果 Map 尚未包含該鍵,Dart 會新增該條目。如果鍵已存在,Dart 會更新其值。
final gifts = {'first': 'partridge'};
gifts['second'] = 'turtle'; // Gets added
gifts['second'] = 'turtle doves'; // Gets updated使用 addAll 方法新增另一個 Map。使用 addEntries 方法將其他條目新增到 Map。
final gifts = {'first': 'partridge'};
gifts['second'] = 'turtle doves';
gifts.addAll({
'second': 'turtle doves',
'fifth': 'golden rings',
});
gifts.addEntries([
MapEntry('second', 'turtle doves'),
MapEntry('fifth', 'golden rings'),
]);使用 remove 方法從 Map 中移除條目。使用 removeWhere 方法移除所有滿足給定測試的條目。
final gifts = {'first': 'partridge'};
gifts.remove('first');
gifts.removeWhere((key, value) => value == 'partridge');使用 length 獲取 Map 中的鍵值對數量。
final gifts = {'first': 'partridge'};
gifts['fourth'] = 'calling birds';
assert(gifts.length == 2);使用 isEmpty 檢查 Map 是否為空。
final gifts = {};
assert(gifts.isEmpty);使用 isNotEmpty 檢查 Map 是否不為空。
final gifts = {'first': 'partridge'};
assert(gifts.isNotEmpty);不可修改
#純 JavaScript 不支援不變性。Dart 提供了多種方法來使陣列、集合或字典等集合不可變。
- 如果集合是編譯時常量且不應被修改,請使用
const關鍵字:
const fruits = <String>{'apple', 'orange', 'pear'}; - 將
Set賦值給一個final欄位,這意味著Set本身不必是編譯時常量。這確保了該欄位不能被另一個Set覆蓋,但仍允許修改Set的大小或內容。
final fruits = <String>{'apple', 'orange', 'pear'}; - 使用
unmodifiable建構函式(如下例所示)建立集合型別的最終版本。這會建立一個不能更改其大小或內容的集合。
final _set = Set<String>.unmodifiable(['a', 'b', 'c']);
final _list = List<String>.unmodifiable(['a', 'b', 'c']);
final _map = Map<String, String>.unmodifiable({'foo': 'bar'});擴充套件運算子
#與 JavaScript 一樣,Dart 支援使用擴充套件運算子 (...) 和空感知擴充套件運算子 (...?) 將列表嵌入到另一個列表中。
var list1 = [1, 2, 3];
var list2 = [0, ...list1]; // [0, 1, 2, 3]
// When the list being inserted could be null:
list1 = null;
var list2 = [0, ...?list1]; // [0]這也適用於 Set 和 Map:
// Spread operator with maps
var map1 = {'foo': 'bar', 'key': 'value'};
var map2 = {'foo': 'baz', ...map1}; // {foo: bar, key: value}
// Spread operator with sets
var set1 = {'foo', 'bar'};
var set2 = {'foo', 'baz', ...set1}; // {foo, baz, bar}集合 if/for
#在 Dart 中,for 和 if 關鍵字在處理集合時具有額外功能。
集合 if 語句僅在滿足指定條件時才包含列表字面量中的項:
var nav = [
'Home',
'Furniture',
'Plants',
if (promoActive) 'Outlet',
];它對 Map 和 Set 也類似工作。
集合 for 語句允許將多個項對映到另一個列表中:
var listOfInts = [1, 2, 3];
var listOfStrings = [
'#0',
for (var i in listOfInts) '#$i',
]; // [#0, #1, #2, #3]這對於 Map 和 Set 也以同樣的方式工作。
非同步
#與 JavaScript 類似,Dart 虛擬機器 (VM) 執行一個單一的事件迴圈來處理所有 Dart 程式碼。這意味著類似的非同步規則也適用於此。您的所有程式碼都是同步執行的,但您可以以不同的順序處理它,這取決於您如何使用可用的非同步工具。以下是其中一些構造及其與 JavaScript 對應物的關係。
Future
#Future 是 Dart 版本 JavaScript 的 Promise。兩者都是非同步操作的結果,該操作將在稍後解析。
Dart 或 Dart 包中的函式可能返回一個 Future,而不是它們所代表的值,因為該值可能要到稍後才能可用。
以下示例顯示了在 Dart 中處理 Future 的方式與在 JavaScript 中處理 Promise 的方式相同。
const httpResponseBody = func();
httpResponseBody.then(value => {
console.log(
`Promise resolved to a value: ${value}`
);
});Future<String> httpResponseBody = func();
httpResponseBody.then((String value) {
print('Future resolved to a value: $value');
});類似地,Future 可能會像 Promise 一樣失敗。捕獲錯誤的工作方式也相同:
httpResponseBody
.then(...)
.catch(err => {
console.log(
"Promise encountered an error before resolving."
);
});httpResponseBody
.then(...)
.catchError((err) {
print(
'Future encountered an error before resolving.'
);
});您還可以建立 Future。要建立 Future,請定義並呼叫一個 async 函式。當您有一個需要成為 Future 的值時,請按照以下示例轉換函式。
String str = 'String Value';
Future<String> strFuture = Future<String>.value(str);Async/Await
#如果您熟悉 JavaScript 中的 Promise,那麼您可能也熟悉 async/await 語法。此語法在 Dart 中是相同的:函式被標記為 async,並且 async 函式總是返回一個 Future。如果函式返回 String 並被標記為 async,它會返回 Future<String>。如果它不返回任何內容,但它是 async,它會返回 Future<void>。
以下示例展示瞭如何編寫一個 async 函式:
// Returns a Promise of a string,
// as the method is async
async fetchString() {
// Typically some other async
// operations would be done here.
return "String Value";
}// Returns a future of a string,
// as the method is async
Future<String> fetchString() async {
// Typically some other async
// operations would be done here.
return 'String Value';
}如下呼叫此 async 函式:
Future<String> stringFuture = fetchString();
stringFuture.then((String str) {
print(str); // 'String Value'
});使用 await 關鍵字獲取 Future 的值。與 JavaScript 一樣,這消除了在 Future 上呼叫 then 以獲取其值的需要,並且它允許您以更像同步程式碼的方式編寫非同步程式碼。與 JavaScript 一樣,只有在 async 上下文(例如另一個 async 函式)中才能等待 Future。
以下示例展示瞭如何等待 Future 以獲取其值:
// We can only await futures within an async context.
Future<void> asyncFunction() async {
var str = await fetchString();
print(str); // 'String Value'
}要了解有關 Future 和 async/await 語法的更多資訊,請參閱 非同步程式設計 教程。
Stream
#Dart 非同步工具箱中的另一個工具是 Stream。雖然 JavaScript 有自己的 Stream 概念,但 Dart 的 Stream 更類似於 Observable,就像常用 rxjs 庫中的那樣。如果您熟悉這個庫,那麼 Dart 的 Stream 應該會讓您感到熟悉。
對於不熟悉這些概念的人來說:Stream 基本功能類似 Future,但它具有隨時間推移分散的多個值,就像一個事件匯流排。您的程式碼可以監聽一個 Stream,它既可以完成也可以達到失敗狀態。
監聽
#要監聽 Stream,請呼叫其 listen 方法並提供一個回撥方法。每當 Stream 發出一個值時,Dart 都會呼叫此方法。
Stream<int> stream = ...
stream.listen((int value) {
print('A value has been emitted: $value');
});listen 方法包含用於處理錯誤或 Stream 完成時的可選回撥函式:
stream.listen(
(int value) { ... },
onError: (err) {
print('Stream encountered an error! $err');
},
onDone: () {
print('Stream completed!');
},
);listen 方法返回一個 StreamSubscription 例項,您可以使用它來停止監聽 Stream。
StreamSubscription subscription = stream.listen(...);
subscription.cancel();這並非監聽 Stream 的唯一方式。與 Future 的 async/await 語法類似,您可以在 async 上下文中將 Stream 與 for-in 迴圈結合使用。for 迴圈會為每個發出的項呼叫回撥方法,並在 Stream 完成或出錯時結束。
Future<int> sumStream(Stream<int> stream) async {
var sum = 0;
await for (final value in stream) {
sum += value;
}
return sum;
}當以這種方式監聽 Stream 時發生錯誤,錯誤會在包含 await 關鍵字的行重新丟擲。您可以使用 try-catch 語句處理此錯誤:
try {
await for (final value in stream) { ... }
} catch (err) {
print('Stream encountered an error! $err');
}建立 Stream
#與 Future 類似,您有多種不同的方式來建立 Stream。Stream 類具有實用建構函式,可用於從 Future 或 Iterable 建立 Stream,或建立在定時間隔發出值的 Stream。要了解更多資訊,請參閱 Stream API 頁面。
StreamController
#實用類 StreamController 可以建立和控制 Stream。其 stream 屬性暴露了它控制的 Stream。其方法提供了向該 Stream 新增事件的方式。
例如,add 方法可以發出新項,而 close 方法會完成 Stream。
以下示例展示了 Stream 控制器的基本用法:
var listeners = 0;
StreamController<int>? controller;
controller = StreamController<int>(
onListen: () {
// Emit a new value every time the stream gets a new listener.
controller!.add(listeners++);
// Close the stream after the fifth listener.
if (listeners > 5) controller.close();
}
);
// Get the stream for the stream controller
var stream = controller.stream;
// Listen to the stream
stream.listen((int value) {
print('$value');
});非同步生成器
#非同步生成器函式可以建立 Stream。這些函式類似於同步生成器函式,但使用 async* 關鍵字並返回一個 Stream。
在非同步生成器函式中,yield 關鍵字將給定值發出到 Stream。然而,yield* 關鍵字與 Stream 而不是其他 Iterable 一起工作。這允許來自其他 Stream 的事件被髮出到此 Stream。在以下示例中,函式在新發出的 Stream 完成後繼續執行。
Stream<int> asynchronousNaturalsTo(int n) async* {
var k = 0;
while (k < n) yield k++;
}
Stream<int> stream = asynchronousNaturalsTo(5);
// Prints each of 0 1 2 3 4 in succession.
stream.forEach(print(value));在 非同步程式設計 文件中瞭解有關 Future、Stream 和其他非同步功能的更多資訊。
類
#表面上看,Dart 中的類與 JavaScript 中的類相似,儘管 JavaScript 類在技術上更像是原型的包裝器。在 Dart 中,類是語言的標準特性。本節涵蓋了 Dart 中類的定義和使用,以及它們與 JavaScript 的不同之處。
"this" 上下文
#Dart 中的 this 關鍵字比 JavaScript 中的更直接。在 Dart 中,您不能將函式繫結到 this,並且 this 從不依賴於執行上下文(JavaScript 中會)。在 Dart 中,this 僅在類內部使用,並且始終指向當前例項。
建構函式
#本節討論 Dart 中的建構函式與 JavaScript 的不同之處。
標準建構函式
#標準類建構函式看起來與 JavaScript 建構函式非常相似。在 Dart 中,constructor 關鍵字被完整的類名取代,並且所有引數都必須顯式型別化。在 Dart 中,new 關鍵字曾經是建立類例項所必需的,但現在是可選的,不再推薦使用。
class Point {
final double x;
final double y;
Point(double x, double y) : this.x = x, this.y = y { }
}
// Create a new instance of the Point class
Point p = Point(3, 5);初始化列表
#使用初始化列表編寫您的建構函式。將初始化列表插入到建構函式的引數和函式體之間。
class Point {
...
Point.fromJson(Map<String, double> json)
: x = json['x']!,
y = json['y']! {
print('In Point.fromJson(): ($x, $y)');
}
...
}建構函式引數
#在建構函式中編寫程式碼來賦值類欄位可能會感覺像是在建立樣板程式碼,因此 Dart 有一些語法糖,稱為初始化引數,使這變得更容易。
class Point {
double x;
double y;
// Syntactic sugar for setting x and y
// before the constructor body runs.
Point(this.x, this.y);
}
// Create a new instance of the Point class
Point p = Point(3, 5);與函式類似,建構函式可以選擇接受位置引數或命名引數。
class Point {
...
// With an optional positioned parameter
Point(this.x, [this.y = 5]);
// With named parameters
Point({ required this.y, this.x = 5 });
// With both positional and named parameters
Point(int x, int y, { boolean multiply }) {
...
}
...
}命名建構函式
#與 JavaScript 不同,Dart 允許類擁有多個建構函式,透過允許您命名它們。您可以選擇擁有一個單個的未命名建構函式,任何額外的建構函式都必須是命名的。
const double xOrigin = 0;
const double yOrigin = 0;
class Point {
double x = 0;
double y = 0;
Point(this.x, this.y);
// Named constructor
Point.origin()
: x = xOrigin,
y = yOrigin;
}Const 建構函式
#要啟用不可變類例項,請使用 const 建構函式。帶有 const 建構函式的類只能有 final 例項變數。
class ImmutablePoint {
final double x, y;
const ImmutablePoint(this.x, this.y);
}建構函式重定向
#您可以從其他建構函式呼叫建構函式,以防止程式碼重複或為引數新增額外的預設值。
class Point {
double x, y;
// The main constructor for this class.
Point(this.x, this.y);
// Delegates to the main constructor.
Point.alongXAxis(double x) : this(x, 0);
}工廠建構函式
#當您不需要建立新的類例項時,可以使用工廠建構函式。一個例子是返回快取例項時。
class Logger {
static final Map<String, Logger> _cache =
<String, Logger>{};
final String name;
// Factory constructor that returns a cached copy,
// or creates a new one if it is not yet available.
factory Logger(String name) {
return _cache.putIfAbsent(
name, () => _cache[name] ??= Logger._internal(name);
}
// Private constructor for internal use only
Logger._internal(this.name);
}方法
#在 Dart 和 JavaScript 中,方法都充當為物件提供行為的函式。
function doSomething() { // This is a function
// Implementation..
}
class Example {
doSomething() { // This is a method
// Implementation..
}
}void doSomething() { // This is a function
// Implementation..
}
class Example {
void doSomething() { // This is a method
// Implementation..
}
}擴充套件類
#Dart 允許類擴充套件另一個類,方式與 JavaScript 相同。
class Animal {
int eyes;
Animal(this.eyes);
makeNoise() {
print('???');
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
Cat(): super(2);
@override
makeNoise() {
print('Meow');
}
}
Animal animal = Cat();
print(animal.eyes); // 2
animal.makeNoise(); // Meow當覆蓋父類中的方法時,使用 @override 註解。雖然此註解是可選的,但它表明覆蓋是故意的。如果方法實際上沒有覆蓋超類方法,Dart 分析器會顯示警告。
被覆蓋的父方法仍然可以使用 super 關鍵字呼叫。
class Cat extends Animal {
...
@override
makeNoise() {
print('Meow');
super.makeNoise();
}
}
Animal animal = Cat();
animal.makeNoise(); // Meow
// ???作為介面的類
#與 JavaScript 類似,Dart 沒有單獨的介面定義。然而,與 JavaScript 不同的是,所有類定義都兼作介面;您可以使用 implements 關鍵字將類作為介面實現。
當一個類被實現為介面時,它的公共 API 必須由新類實現。與 extends 不同,它的方法和欄位實現不會與新類共享。雖然一個類只能擴充套件一個類,但您可以同時實現多個介面,即使實現類已經擴充套件了另一個類。
class Consumer {
consume() {
print('Eating food...');
}
}
class Cat implements Consumer {
consume() {
print('Eating mice...');
}
}
Consumer consumer = Cat();
consumer.consume(); // Eating mice實現介面時,不能呼叫 super 方法,因為方法體未被繼承。
class Cat implements Consumer {
@override
consume() {
print('Eating mice...');
super.consume();
// Invalid. The superclass `Object` has no `consume` method.
}
}抽象類與方法
#為了確保一個類只能被擴充套件或實現其介面,但禁止構造任何例項,請將其標記為 abstract。
被標記為 abstract 的類可以擁有抽象方法,這些方法不需要函式體,而是在類被擴充套件或其介面被實現時才需要實現。
abstract class Consumer {
consume();
}
// Extending the full class
class Dog extends Consumer {
consume() {
print('Eating cookies...');
}
}
// Just implementing the interface
class Cat implements Consumer {
consume() {
print('Eating mice...');
}
}
Consumer consumer;
consumer = Dog();
consumer.consume(); // Eating cookies...
consumer = Cat();
consumer.consume(); // Eating mice...混入
#混入(Mixin)用於在類之間共享功能。您可以在類中使用混入的欄位和方法,就像它們是類的一部分一樣。一個類可以使用多個混入。當多個類共享相同功能,而無需相互繼承或共享共同祖先時,這很有幫助。
使用 with 關鍵字向類新增一個或多個以逗號分隔的混入。
JavaScript 沒有等效的關鍵字。JavaScript 可以在例項化後使用 Object.assign 將其他物件合併到現有物件中。
以下示例展示了 JavaScript 和 Dart 如何實現類似的行為:
class Animal {}
// Defining the mixins
class Flyer {
fly = () => console.log('Flaps wings');
}
class Walker {
walk = () => console.log('Walks on legs');
}
class Bat extends Animal {}
class Goose extends Animal {}
class Dog extends Animal {}
// Composing the class instances with
// their correct functionality.
const bat =
Object.assign(
new Bat(),
new Flyer()
);
const goose =
Object.assign(
new Goose(),
new Flyer(),
new Walker()
);
const dog =
Object.assign(
new Dog(),
new Walker()
);
// Correct calls
bat.fly();
goose.fly();
goose.walk();
dog.walk();
// Incorrect calls
bat.walk(); // `bat` lacks the `walk` method
dog.fly(); // `dog` lacks the `fly` methodabstract class Animal {}
// Defining the mixins
class Flyer {
fly() => print('Flaps wings');
}
class Walker {
walk() => print('Walks on legs');
}
class Bat extends Animal with Flyer {}
class Goose extends Animal with Flyer, Walker {}
class Dog extends Animal with Walker {}
// Correct calls
Bat().fly();
Goose().fly();
Goose().walk();
Dog().walk();
// Incorrect calls
Bat().walk(); // Not using the Walker mixin
Dog().fly(); // Not using the Flyer mixin或者,您可以將 class 關鍵字替換為 mixin,以防止混入被用作常規類。
mixin Walker {
walk() => print('Walks legs');
}
// Not possible, as Walker is no longer a class.
class Bat extends Walker {}由於您可以使用多個混入,因此當在同一個類上使用時,它們之間可以有重疊的方法或欄位。它們甚至可以與使用它們的類或該類的超類重疊。它們新增到類中的順序很重要。
舉個例子:
class Bird extends Animal with Consumer, Flyer {當在 Bird 的例項上呼叫方法時,Dart 會從它自己的類 Bird 開始,它優先於其他實現。如果 Bird 沒有實現,則檢查 Flyer,然後是 Consumer,直到找到實現。父類 Animal 最後被檢查。
擴充套件
#擴充套件類、實現介面或使用混入在受影響的類可編輯時都有效。然而,有時擴充套件一個已存在的類或屬於另一個庫或 Dart SDK 的類會很有用。
在這些情況下,Dart 提供了為現有類編寫擴充套件的能力。
例如,以下對 Dart SDK 中 String 類的擴充套件允許解析整數:
extension NumberParsing on String {
int parseInt() {
return int.parse(this);
}
}要使擴充套件可用,它必須存在於同一檔案中,或其檔案必須被匯入。
使用方法如下:
import 'string_apis.dart'; // Import the file the extension is in
var age = '42'.parseInt(); // Use the extension method.Getter 與 Setter
#Dart 中的 Getter 和 Setter 工作方式與其 JavaScript 對應物完全相同。
class Person {
_age = 0;
get age() {
return this._age;
}
set age(value) {
if (value < 0) {
throw new Error(
'age cannot be negative'
);
}
this._age = value;
}
}
var person = new Person();
person.age = 10;
console.log(person.age);class Person {
int _age = 0;
int get age {
return _age;
}
set age(int value) {
if (value < 0) {
throw ArgumentError(
'Age cannot be negative'
);
}
_age = value;
}
}
void main() {
var person = Person();
person.age = 10;
print(person.age);
}公共和私有成員
#與 JavaScript 類似,Dart 沒有訪問修飾符關鍵字:所有類成員預設都是公共的。
JavaScript 將在 EcmaScript 標準的下一個實際修訂版中包含私有類成員。因此,此功能的一些實現已經在各種瀏覽器和執行時中存在了一段時間。
要在 JavaScript 中使類成員私有化,請在其名稱前加上井號 (#)。
class Animal {
eyes; // Public field
#paws; // Private field
#printEyes() { // Private method
print(this.eyes);
}
printPaws() { // Public method
print(this.#paws);
}
}要在 Dart 中使類成員私有化,請在其名稱前加上下劃線 (_)。
class Animal {
int eyes; // Public field
int _paws; // Private field
void _printEyes() { // Private method
print(this.eyes);
}
void printPaws() { // Public method
print(this._paws);
}
}JavaScript 使用井號作為約定。Dart 的編譯器強制要求使用下劃線來實現此功能。
Dart 將私有成員私有化到庫,而不是類。這意味著您可以從同一庫中的程式碼訪問私有成員。預設情況下,Dart 將對私有類成員的訪問限制在同一檔案中的程式碼。要將庫的範圍擴充套件到一個檔案之外,請新增 part 指令。如果可能,請避免使用 part。將 part 的使用保留給程式碼生成器。
Late 變數
#要指示 Dart 在稍後初始化類欄位,請將 late 關鍵字賦給這些類欄位。這些類欄位保持非可空。當變數不需要立即觀察或訪問,並且可以在以後初始化時,執行此操作。這與將欄位標記為可空不同。
(非空)
late欄位不能在稍後被賦值為 null。(非空)
late欄位在初始化之前被訪問時會丟擲執行時錯誤。應避免這種情況。
class PetOwner {
final String name;
late final Pet _pet;
PetOwner(this.name, String petName) {
// Cyclic object graph, cannot set _pet before owner exists.
_pet = Pet(petName, this);
}
Pet get pet => _pet;
}
class Pet {
final String name;
final PetOwner owner;
Pet(this.name, this.owner);
}僅當代碼不明確導致編譯器無法確定變數是否已初始化時,才對區域性變數使用 late。
doSomething(int n, bool capture) {
late List<Foo> captures;
if (capture) captures = [];
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var foo = something(i);
if (capture) captures.add(foo);
}
}在前面的示例中,如果 capture 為 true,編譯器不知道是否要賦值 captures。使用 late 會將正常的“已賦值”檢查延遲到執行時。
泛型
#雖然 JavaScript 不提供泛型,但 Dart 提供泛型以提高型別安全並減少程式碼重複。
泛型方法
#您可以將泛型應用於方法。要定義泛型型別引數,請將其放在方法名稱後的尖括號 < > 中。然後,您可以在方法內部將其用作返回型別或在方法的引數中使用它。
Map<Object?, Object?> _cache = {};
T cache<T>(T value) => (_cache[value] ??= value) as T;透過逗號分隔來定義多個泛型型別:
// Defining a method with multiple generics.
T transform<T, Q>(T param1, Q param2) {
...
}
// Calling the method with explicitly defined types.
transform<int, String>(5, 'string value');
// Types are optional when the analyzer can infer them.
transform(5, 'string value');泛型類
#泛型也可以應用於類。您可以在呼叫建構函式時包含要使用的型別。這使您能夠根據特定型別定製可重用類。
在以下示例中,Cache 類快取特定型別:
class Cache<T> {
T getByKey(String key) {}
void setByKey(String key, T value) {}
}
// Creating a cache for strings
var stringCache = Cache<String>(); // stringCache has type Cache<String>
stringCache.setByKey('Foo', 'Bar'); // Valid, setting a string value.
stringCache.setByKey('Baz', 5); // Invalid, int type does not match generic.如果您省略型別宣告,執行時型別將變為 Cache<dynamic>,並且對 setByKey 的兩次呼叫都有效。
限制泛型
#您可以使用泛型透過 extends 將程式碼限制為一系列型別。這確保了您的類使用擴充套件特定型別的泛型型別例項化。
class NumberManager<T extends num> {
...
}
// Valid.
var manager = NumberManager<int>();
var manager = NumberManager<double>();
// Invalid, String nor its parent classes extend num.
var manager = NumberManager<String>();字面量中的泛型
#Map、Set 和 List 字面量可以接受型別引數。當 Dart 無法推斷型別或無法正確推斷型別時,這很有幫助。
例如,List 類有一個泛型定義:class List<E>。型別引數 E 指的是列表內容的型別。通常,此型別是自動推斷的,並用於 List 類的一些成員型別中。(例如,它的第一個 getter 返回 E 型別的值。)在定義 List 字面量時,您可以按如下方式顯式定義泛型型別:
// Automatic type inference
var objList = [5, 2.0]; // Type: List<num>
// Explicit type definition:
var objList = <Object>[5, 2.0]; // Type: List<Object>
// Sets work identically:
var objSet = <Object>{5, 2.0};對於 Map 也是如此,它們也使用泛型定義其鍵和值型別 (class Map<K, V>)。
// Automatic type inference
var map = {
'foo': 'bar'
}; // Type: Map<String, String>
// Explicit type definition:
var map = <String, Object>{
'foo': 'bar'
}; // Type: Map<String, Object>文件註釋
#常規註釋在 Dart 中的工作方式與 JavaScript 中相同。使用 // 會註釋掉該行其餘部分的所有內容,您可以使用 /* ... */ 來進行跨多行的塊註釋。
除了常規註釋,Dart 還有與 文件註釋 協同工作的 dart doc:dart doc 是一個生成 Dart 包 HTML 文件的官方工具。將文件註釋放在所有公共成員宣告之上被認為是最佳實踐。
透過使用三個正斜槓而不是兩個 (///) 來定義文件註釋:
/// The number of characters in this chunk when unsplit.
int get length => ...下一步
#本指南向您介紹了 Dart 和 JavaScript 之間的主要區別。現在,您可以考慮閱讀 Dart 文件。您也可以閱讀 Flutter 文件。Flutter 是一個用 Dart 構建的開源框架,它使用 Dart 從單一程式碼庫構建原生編譯的多平臺應用程式。這些文件提供了關於該語言的深入資訊和實用的入門方法。
一些可能的下一步: